New antibodies against coronaviruses
The aim of our research project is to generate "new-generation" antibodies composed of multiple anchoring points in order to effectively block the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the cells. The small size of these antibodies may result in better penetration into the tissues, better management of the viral resistance mechanisms and the production of new drugs.
Background
The COVID-19 pandemic has produced an unprecedented global health and economic crisis. Since no vaccine or therapy was available at the start of the project, developing new treatments was a matter of urgency.
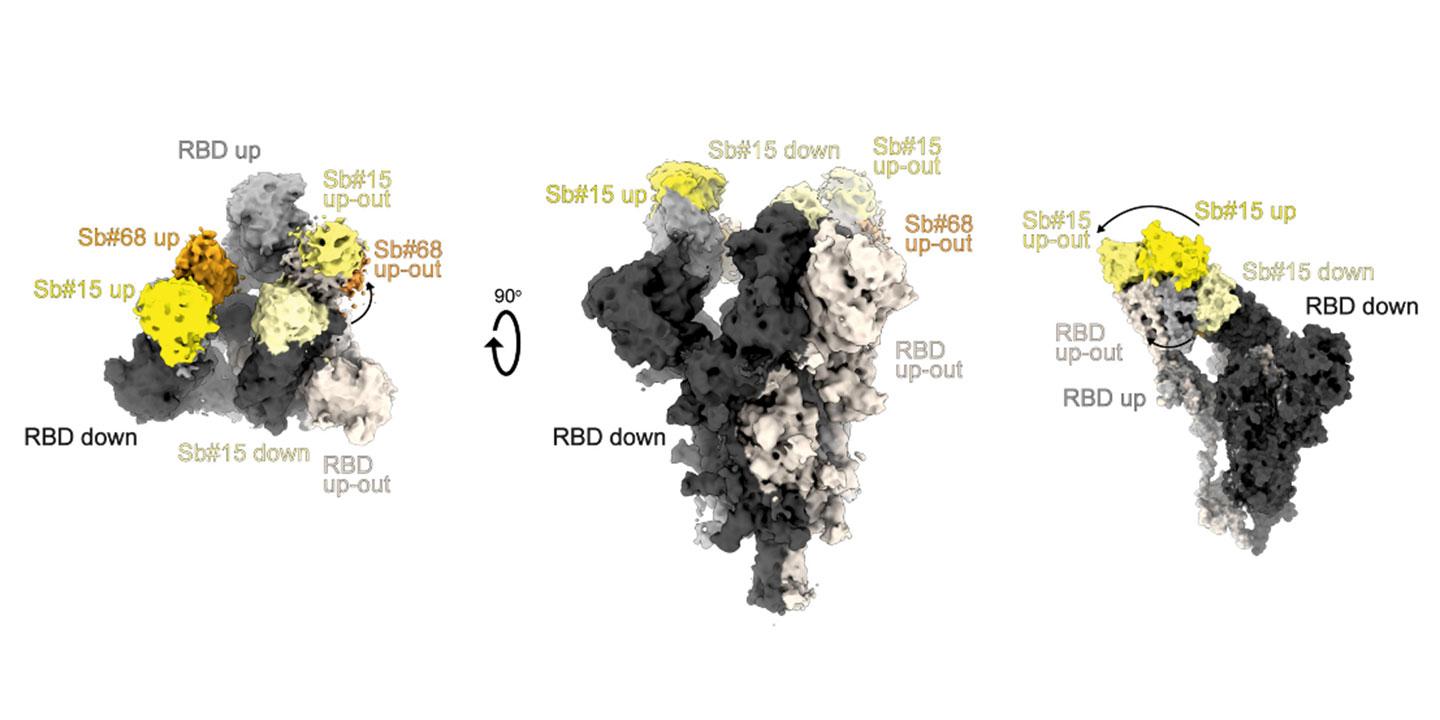
The entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the cell is controlled by the spike protein (S) anchored in the viral envelope. The S protein binds to a receptor located on the target cell, ultimately resulting in the injection of genetic material from the virus into the cell. This S protein is a major target for the production of antibodies by the immune system in response to the infection.Research aims
Our project focuses on the development of "new-generation" neutralising antibodies that block the entry of the virus into the cell. The antibodies generated in this project are designed to contain several mini-domains derived from antibodies produced by llamas. These antibodies are fused together and simultaneously target several functional regions of the S protein.
Expected results and envisaged products
In collaboration with the universities of Bern and Zurich, a panel of "mini-domains" will first be identified using an innovative synthetic platform and then characterised in respect of its biochemistry (affinity studies), structure (molecular localisation of the mini-domains on the S protein by cryo-electron microscopy) and function (viral neutralisation tests). This in-depth characterisation will enable various excellent mini-domains to be selected and then fused, potentially resulting in the production of biomolecules with unprecedented neutralisation efficacy.
Specific contribution to tackle the current pandemic
Such multi-domain antibodies may show unparalleled therapeutic efficacy due to several factors: (i) a neutralising activity superior to conventional antibodies as a result of their multiple anchoring points on the S protein, (ii) a reduction in the risk of developing resistant viruses thanks to the multi-directional attack, (iii) the promising possibility of developing a drug that could be directly inhaled, and (iv) a technological approach for producing neutralising antibodies not just against SARS-CoV-2, but potentially also against other coronaviruses that might emerge in future epidemics or pandemics.
Original title
Neutralizing multivalent antibodies against coronaviruses